BYOM function derivatives.m (the model in ODEs)
Syntax: dX = derivatives(t,X,par,c,glo)
This function calculates the derivatives for the model system. It is linked to the script files byom_bioconc_extra.m and byom_bioconc_start.m. As input, it gets:
- t is the time point, provided by the ODE solver
- X is a vector with the previous value of the states
- par is the parameter structure
- c is the external concentration (or scenario number)
- glo is the structure with information (normally global)
Note: glo is now an input to this function rather than a global. This makes the code considerably faster.
Time t and scenario name c are handed over as single numbers by call_deri.m (you do not have to use them in this function). Output dX (as vector) provides the differentials for each state at t.
- Author: Tjalling Jager
- Date: November 2021
- Web support: http://www.debtox.info/byom.html
- Back to index walkthrough_byom.html
Copyright (c) 2012-2021, Tjalling Jager, all rights reserved. This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the LICENSE.txt file in the root directory of BYOM.
Contents
Start
Note that, in this example, variable c (the scenario identifier) is not used in this function. The treatments differ in their initial exposure concentration that is set in X0mat. Also, the time t and structure glo are not used here.
function dX = derivatives(t,X,par,c,glo)
Unpack states
The state variables enter this function in the vector X. Here, we give them a more handy name.
Cw = X(1); % state 1 is the external concentration Ci = X(2); % state 2 is the internal concentration
Unpack parameters
The parameters enter this function in the structure par. The names in the structure are the same as those defined in the byom script file. The 1 between parentheses is needed for fitting the model, as each parameter has 4-5 associated values.
kd = par.kd(1); % degradation rate constant, d-1 ke = par.ke(1); % elimination rate constant, d-1 Piw = par.Piw(1); % bioconcentration factor, L/kg Ct = par.Ct(1); % threshold external concentration that stops degradation, mg/L % % Optionally, include the threshold concentration as a global (see script) % Ct = glo.Ct; % threshold external concentration that stops degradation, mg/L
Calculate the derivatives
This is the actual model, specified as a system of two ODEs:
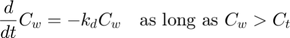

if Cw > Ct % if we are above the critical internal concentration ... dCw = -kd * Cw; % let the external concentration degrade else % otherwise ... dCw = 0; % make the change in external concentration zero end dCi = ke * (Piw * Cw - Ci); % first order bioconcentration dX = [dCw;dCi]; % collect both derivatives in one vector dX